Working Principle-Core Knowledge of Oilless Air Piston Compressors
Over the past few decades, piston technology has remained one of the most widely adopted and versatile solutions for pumps and compressors globally. XWD’s comprehensive product portfolio includes a broad range of oil-free piston compressors and vacuum pumps, designed to meet diverse global market demands.
Mechanical Principles
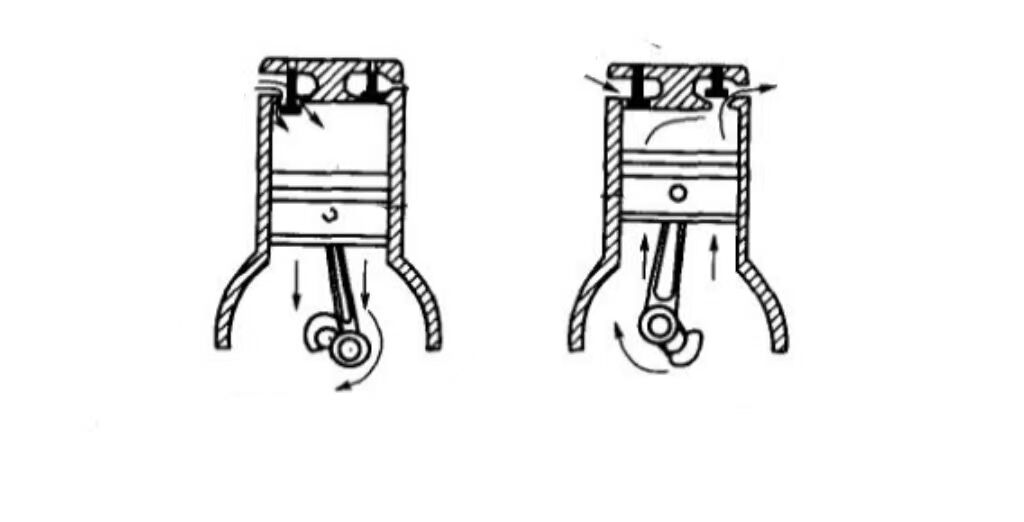
Piston technology operates on the principle of positive displacement. Taking a dual-cylinder design as an example: one end handles gas intake (suction), while the other manages gas discharge (exhaust). The electric motor of the pump or compressor drives the rotation of the crankshaft and connecting rod. The connecting rod converts this rotational motion into reciprocating movement of the piston. As the piston moves up and down within the cylinder, it generates alternating vacuum and pressure.
· Intake Stroke (Suction Phase):
During the downward stroke, the piston creates a vacuum, drawing gas into the cylinder chamber through the open intake valve.
· Compression Stroke (Discharge Phase):
During the upward stroke, the piston compresses the gas, forcing it out through the open exhaust valve.
Core Principles:
· Reciprocating piston motion alters cylinder volume, synchronized with intake/exhaust valves to achieve gas compression.
· Rocking piston compressor mechanisms ensure smooth operation and high efficiency, minimizing wear and vibration.
Thermodynamic Process:
· Follows the ideal gas law. Compression may generate heat, necessitating integrated cooling systems.
Flow Rate (Capacity):
· Measured in L/min or CFM, determined by cylinder size and rotational speed.
Operating Pressure:
· Positive pressure: Bar or PSI / Negative pressure: -kPa or mmHg
Key Features of XWD Oilless Air Compressors:
· Oil-Free Air Compressor Head: Ensures 100% oil-free operation, eliminating contamination risks for sensitive applications like medical devices and food processing.
· Compressor Head Design: Engineered for durability and precision, optimized for low-maintenance, high-performance output.
· Rocking Piston Technology: Reduces mechanical stress and noise, enhancing longevity and reliability.
Maintenance & Troubleshooting
Routine Maintenance:
· Regularly replace wear parts (e.g., diaphragms, seals).
· Inspect valve plates and sealing rings for wear.
· Monitor vibration and abnormal noises; recalibrate crankshaft balance as needed.
Common Issues:
1. Overheating: Caused by blockages or insufficient cooling.
2. Reduced Flow Rate: Due to clogged intake filters or valve leaks.
3. erformance.







